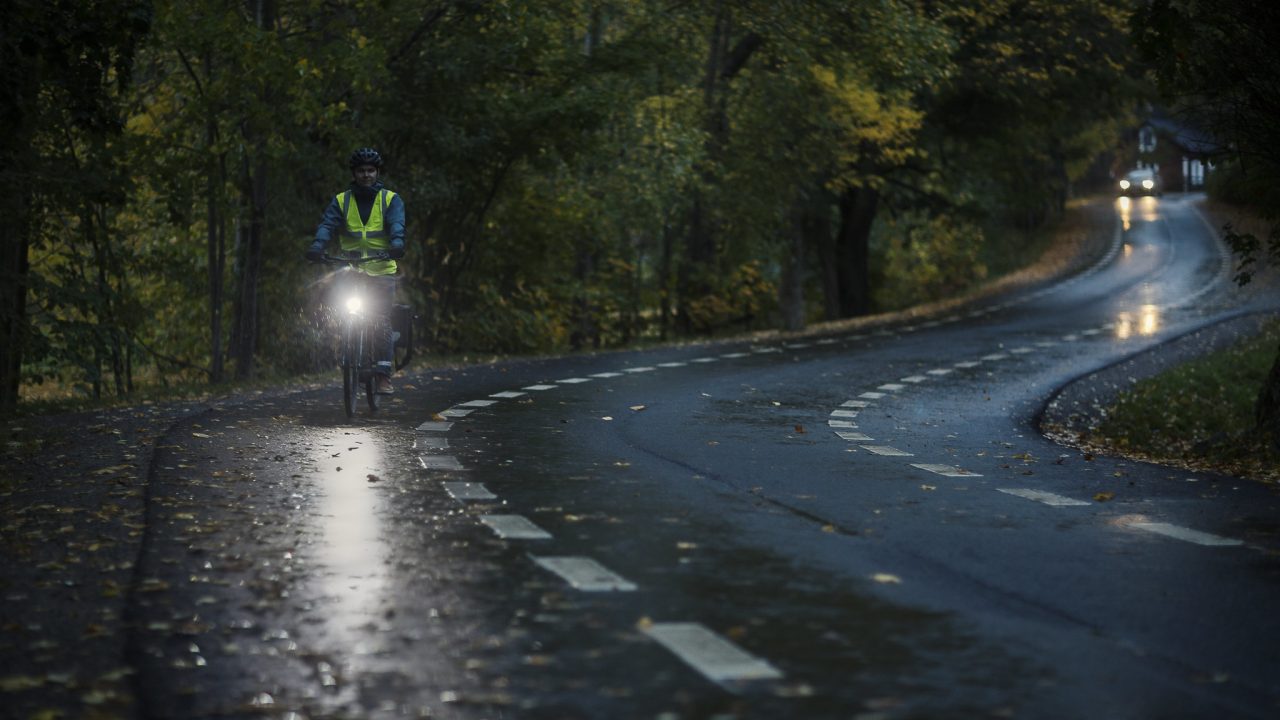

Cycling in Finland
Cycling is a healthy and environmentally friendly way of moving around – and a fast form of transport especially on shorter journeys. When cycling in Finland respect the rules of the road: keep to the right, give way to those coming from your right, ride sober and with a safety conscious attitude.
A cycle is classified as a vehicle and cyclists thus as drivers. This means that as a cyclist you must know and comply with the traffic rules: cyclists, like motorists, must ride on the right side of the road, stop for stop signs and red lights, signal turns, and yield to traffic that has the right-of-way.
Key traffic rules for cyclists are summarised in our On foot and by bike -guide (PDF). (Opens in a new window)
See also a short summary of key points about cycling in Finland (PDF).
Where can you cycle?
In Finland cyclists must use the cycle path if there is one for the direction in which they are travelling. There are separate paths designated for cyclists and shared-use paths, where cyclists and pedestrians use the same paths.
A cycle path is always marked with a road sign.
If there is no cycle path or a cycle lane, a cyclist rides on the verge of the right side of the road. If there is no verge cyclists ride as close to the right side of the road as safety allows. Cyclists ride one behind the other, not side-by-side.
Take note that in Finland it is not allowed to cycle on pedestrian paths. Children under the age of 12 may ride on pavements, but they must give unobstructed passage to pedestrians. Pedestrian paths are not always marked with a separate sign so stay vigilant.
Especially on shared paths, take care when passing pedestrians, especially children, older or disabled people, and allow them plenty of room. Always be prepared to slow down and stop if necessary.
Shared path for pedestrians and cyclists
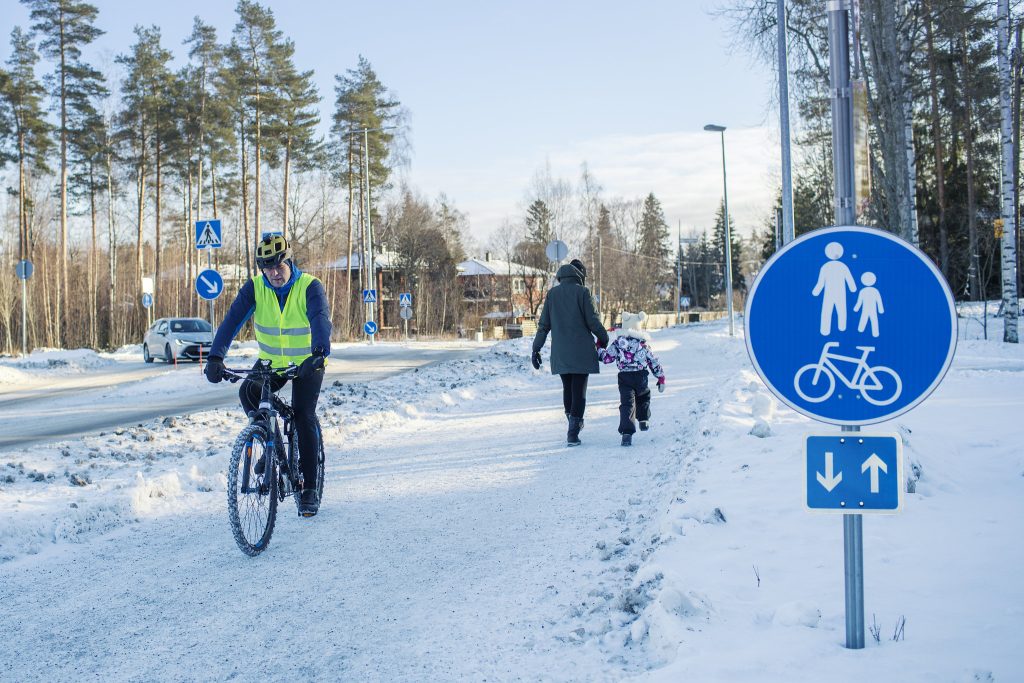

Cyclists ride on the right-hand
side. If overtaking, keep a proper safety distance. Look over your shoulder before overtaking to make sure the road is clear.
Pedestrians can freely choose the side they are walking.
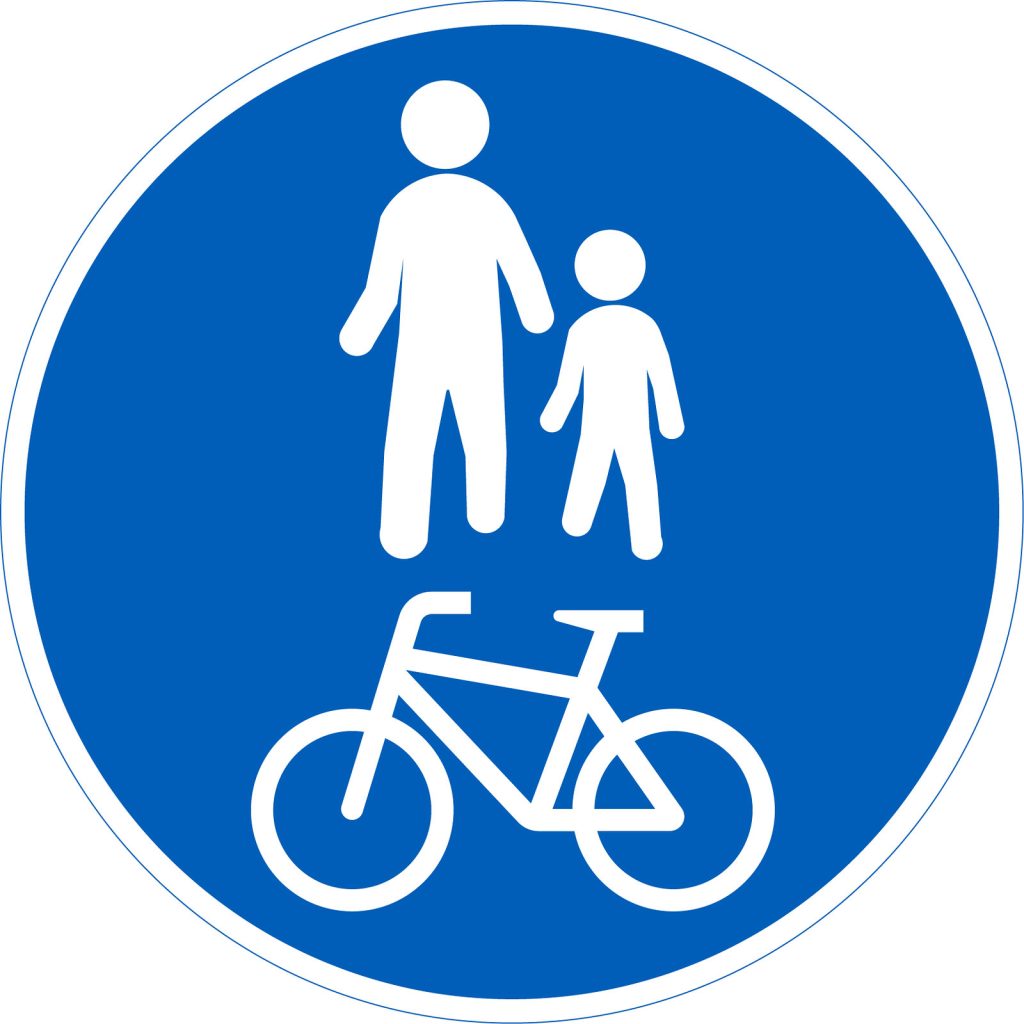

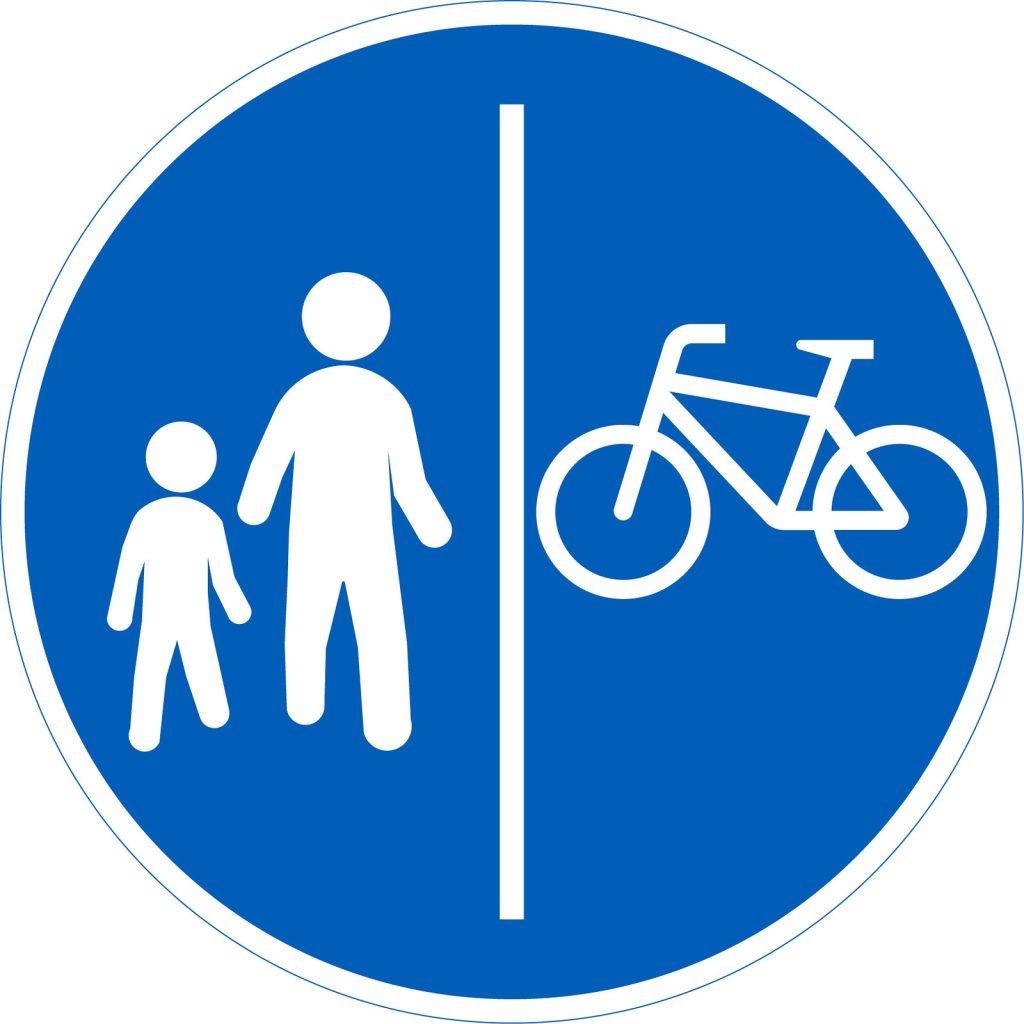
Divided path for pedestrians and cyclists

The road sign indicates which side is for pedestrians and which side is for cyclists.
Cyclists must ride on the right-hand side of their own path.

Cycle path
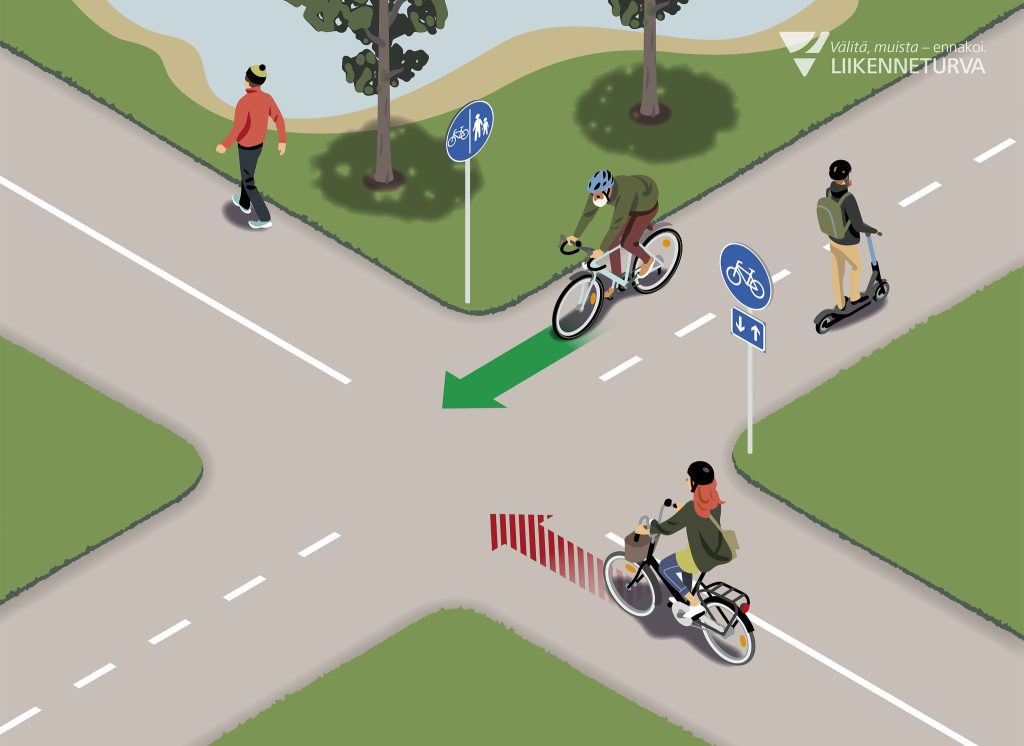
On a cycle path keep to the right. In an intersection, give way to vehicles approaching from the right
unless there is a road sign indicating otherwise.
If there is no pavement, pedestrians may walk on the side of the cycle path.
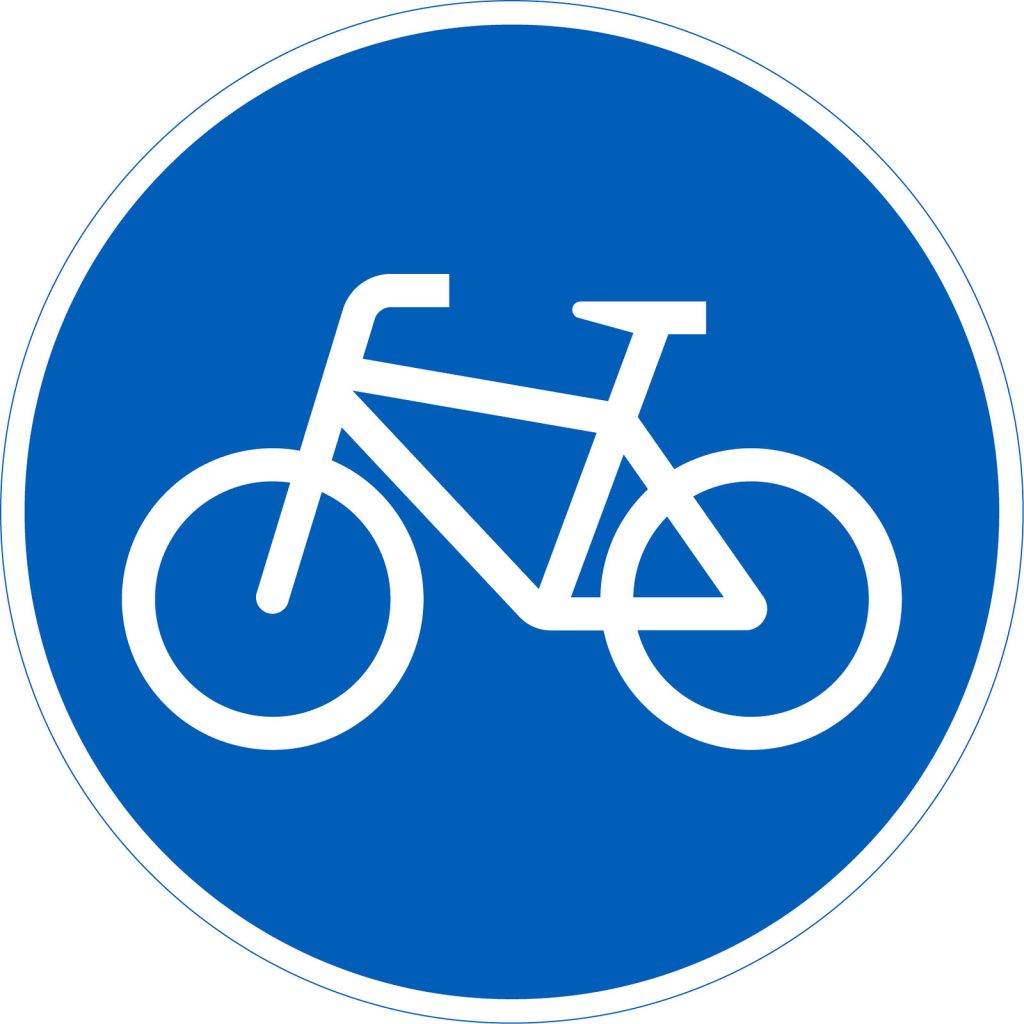

Cycle street
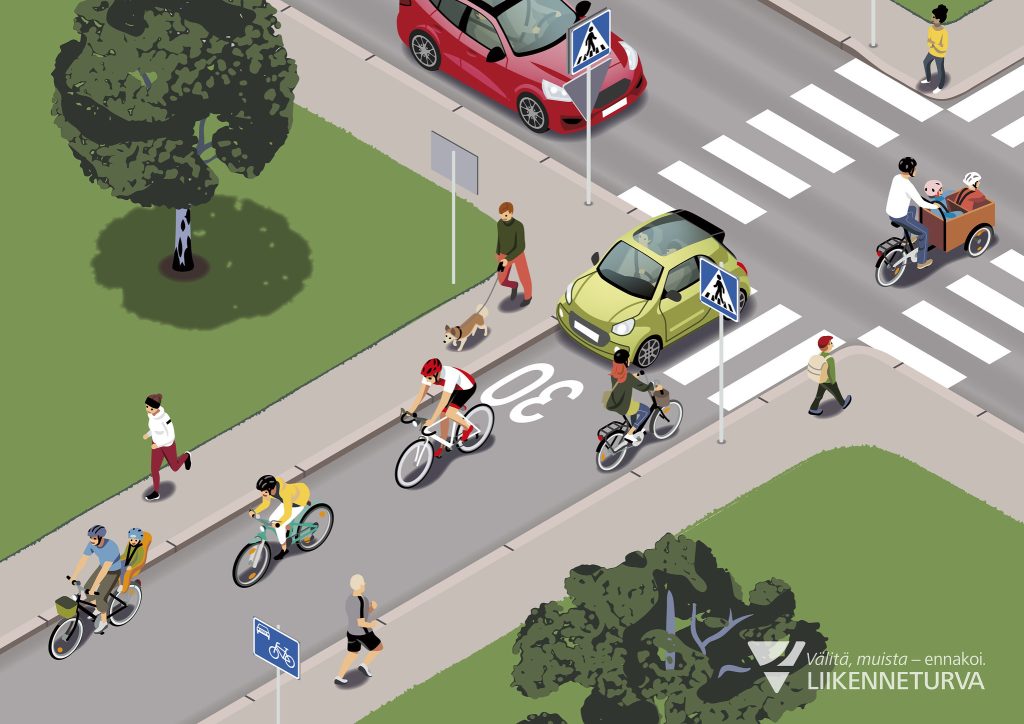
Cars are allowed on a cycle street, but cyclists must be given unobstructed access and the driving speed must be adjusted to cycling speed. The speed limit on the cycle street is indicated with a separate sign.

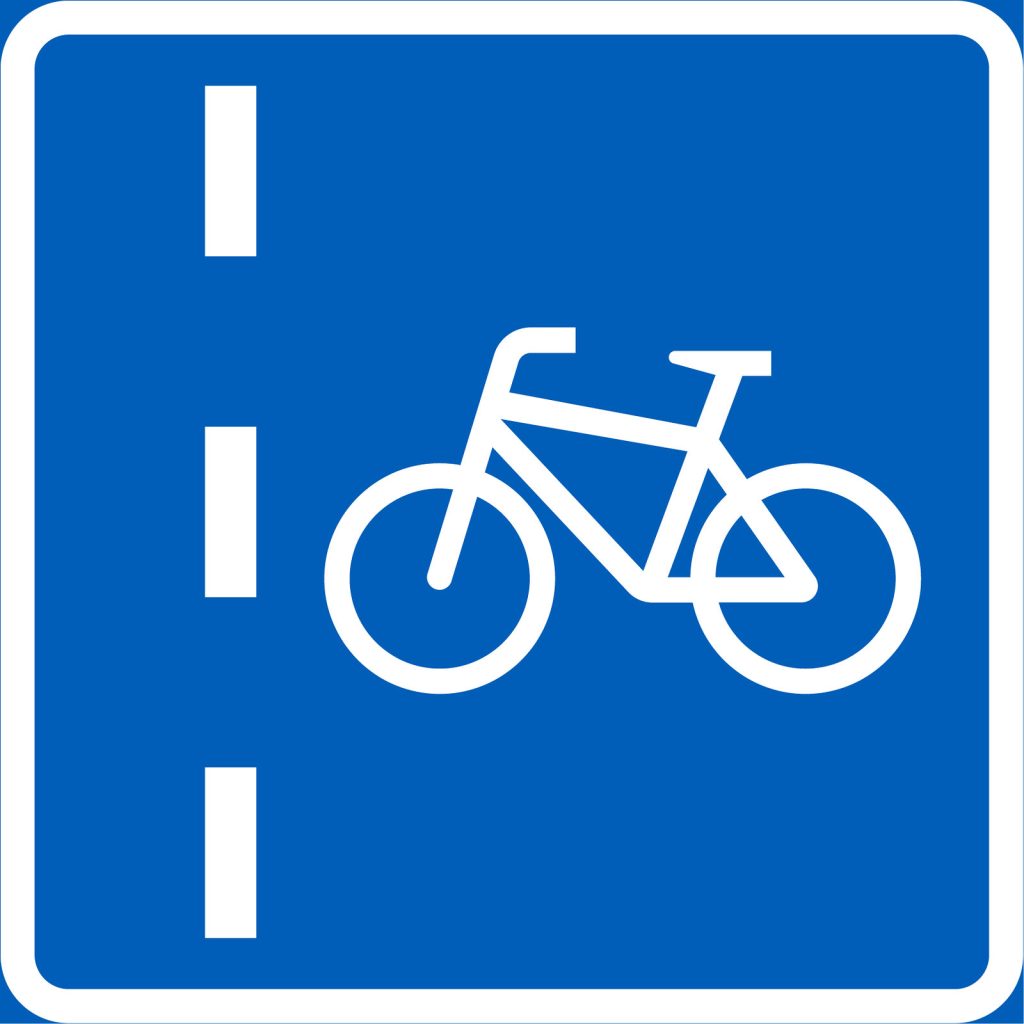
Cycle lane
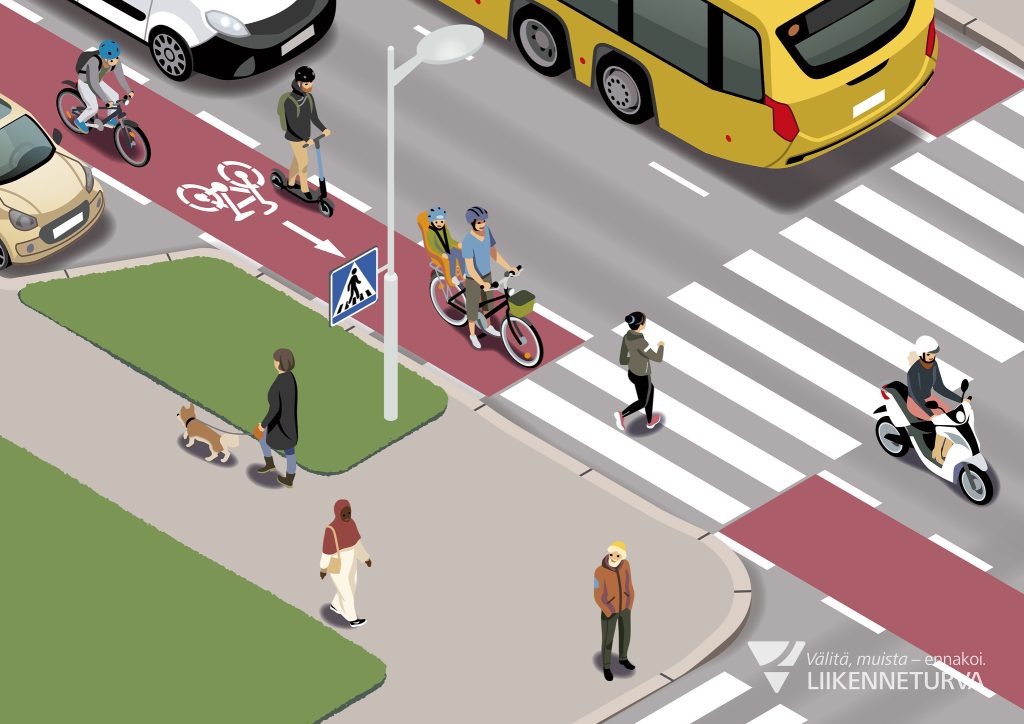

Cycle lane is a lane designated for cyclists on the road. Cycle lanes can be marked with a road sign or road markings or both. When riding on a cycle lane, obey the same rules as riding on a road. Take note of the riding direction and keep a good distance between yourself and parked cars so you don’t get doored.

Cycling on the road
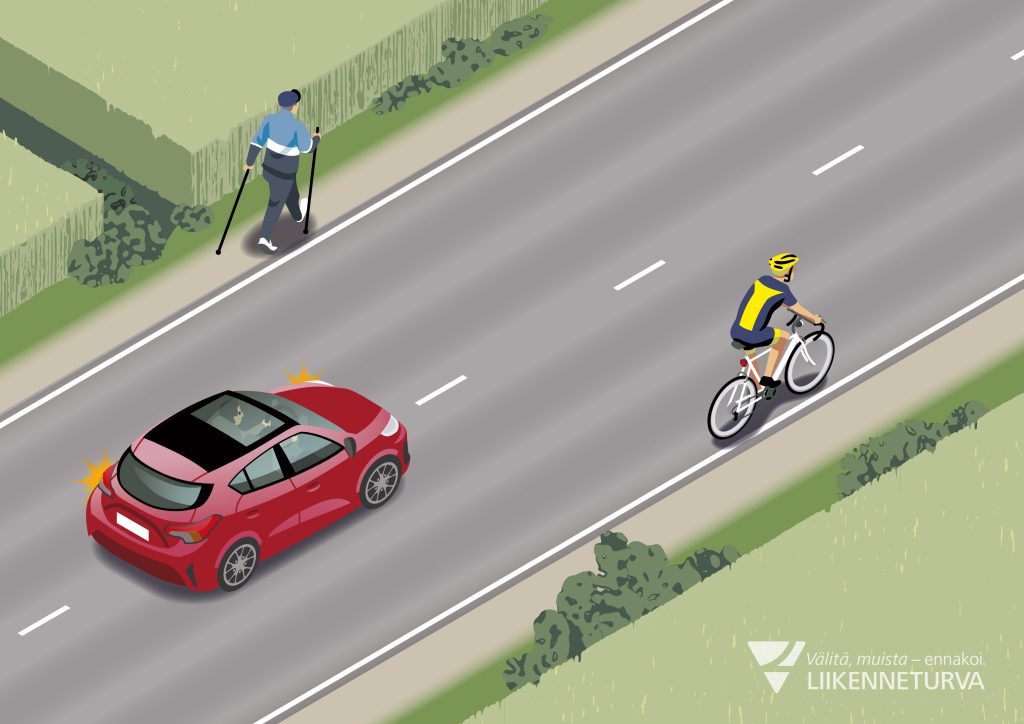

If there is no cycle path or a verge, a cyclist rides as close to the right side of the road as safety allows.
Take note that on the road cyclists ride one behind the other, not side-by-side.
Cycling on the street
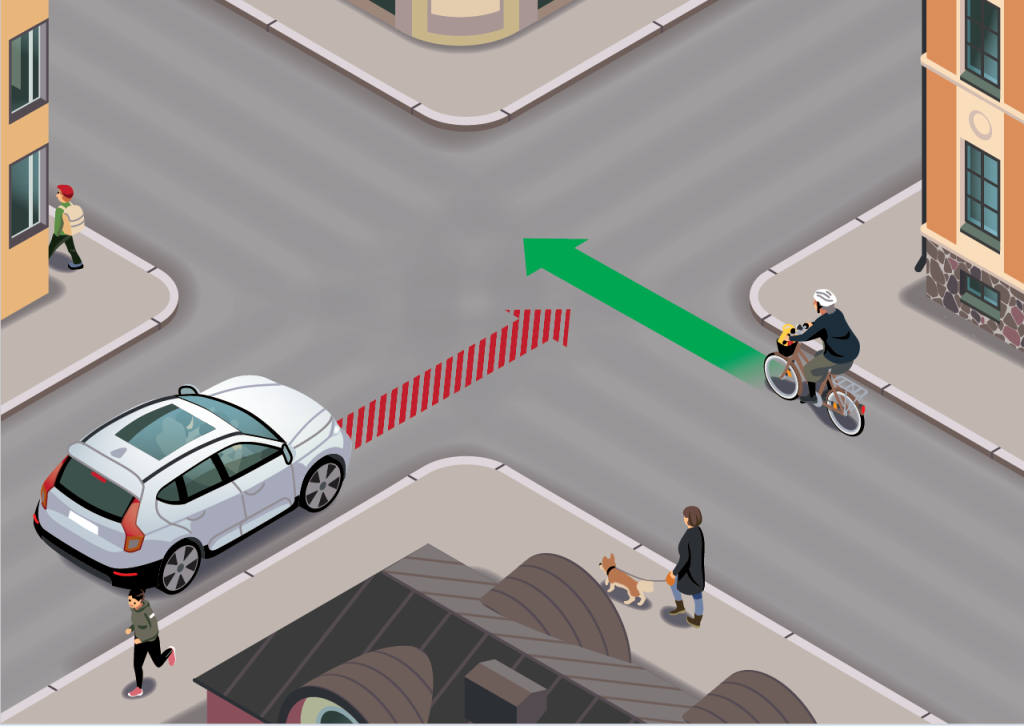
On the street bicyclists are expected to follow the same rules of the road as motorists and ride in the same direction. In the picture on the left the motorist must give way to the cyclist, because the cyclist is coming from the right. See other key rules for cyclists in the On Foot and by Bike -guide.
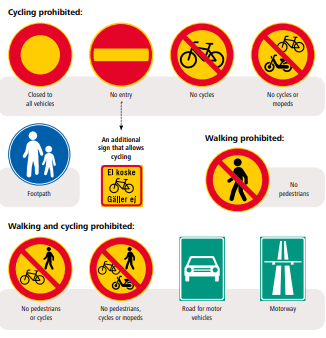
Cycling or walking can also be prohibited with certain signs:
Safe cycling
Safe cycling requires riding skills and the ability to consider other road users and spot potential hazards such as such as potholes, broken glass, gravel, puddles, ice etc. Alertness and focusing on cycling are important. If you need to use your phone, stop at a safe place first. Avoid riding with headphones or an earpiece so you can hear what is happening around you. Pay special attention to pedestrians and give them safe space. When overtaking a pedestrian or another cyclist, keep a safe distance.
Cyclists are responsible for ensuring that they have the necessary ability and fitness to cycle safely. Illnesses, medication, fatigue and intoxication can affect cyclists’ ability to drive. The use of alcohol or drugs increases the risk of a cycling accident.
In Finland cycling drunk is an offence, if the cyclist causes danger to other road users. The offence is punishable by fine or up to three months of imprisonment.
Cyclists have a duty to indicate when turning and give audible warnings (by e.g. ringing the bell) when needed.
By choosing the safest routes and a correct speed a cyclists can improve the safety of the ride. Special attention must be paid at junctions and road crossings, as this is where the majority of collisions between cyclists and car drivers happen, though most cycling accidents in Finland are isolated accidents. The most common type of cycling accident is falling on a slippery or uneven surface. By reducing speed, a cyclist can get more time to spot and react to unexpected situations.
Equipment and roadworthiness
Before riding, make sure your bike is ready to ride, inflate tires properly and check that your brakes and lights are in good working order.
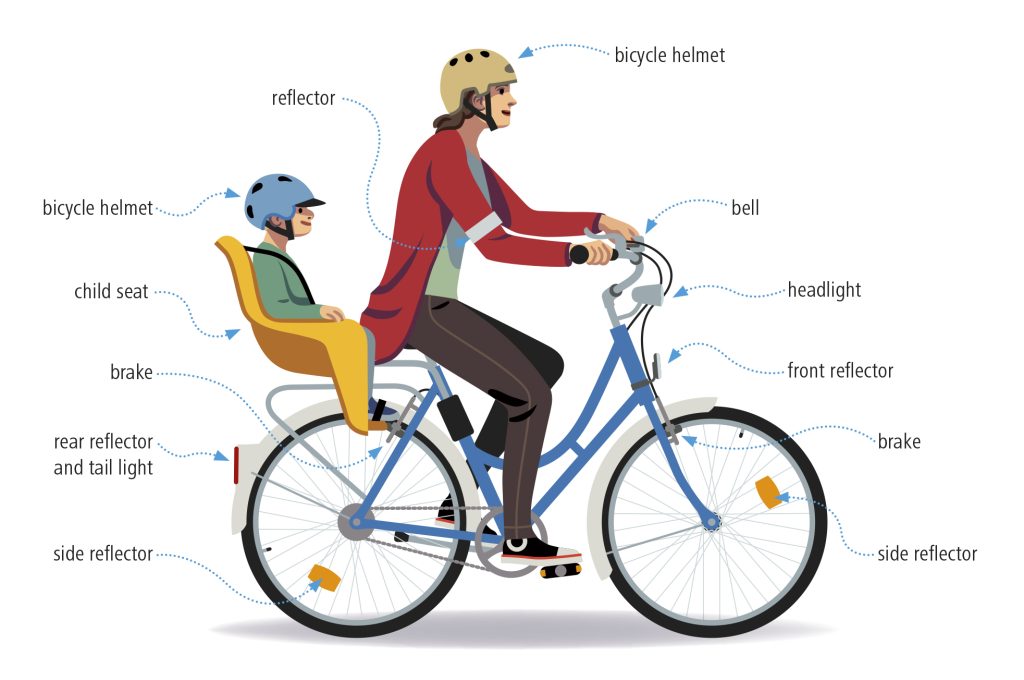
A cycle must have:
- At least one effective braking device. Bicycles that are designed for transporting cargo or passengers must have two separate braking devices. Two devices are also required if towing a bicycle trailer and in bicycles with more than two gears.
- A white front reflector, a red back reflector, and white or brown-yellow side reflectors (or reflective tyres/stickers)
- Lights when cycling after dark or when visibility is poor: a white or light yellow front light and a red rear light. The lights can also be mounted on your helmet or body.
- An audible warning device, such as a bell.
The helmet is important for cyclists’ safety. It protects the cyclist’s head in the event of an accident. Make sure that your helmet is in good condition and securely fastened. The helmet is particularly important in winter when the risk of sliding and falling is higher. A helmet hood under the helmet keeps the head and forehead warm.
Light-coloured or fluorescent clothing can help other road users to see cyclists in daylight and foul weather, while reflective clothing, reflectors or a reflective vest increase visibility in the dark. Reflectors or reflective material sends the car’s light straight back to the driver which helps the cyclists to be seen.
A well-maintained bicycle is safe and comfortable to ride. It requires good brakes and the recommended air pressure in the tyres. Choose the right bicycle for your needs and local conditions.
A secure basket or bike bags are useful for carrying e.g. shopping. If you carry cargo on your bicycle, pay attention to your balance. When the load is distributed evenly on both sides of the bicycle, the bicycle rides more stably and safely.
Cycling in winter
In Finland cold weather can make riding treacherous from September till April. Surfaces can be especially hazardous when the temperature hovers around zero and there is ice under a layer of snow.
If riding in these conditions, be aware of the challenges and handle your bike accordingly:
- Avoid sudden moves. they can easily make the bicycle uncontrollable.
- Be careful at at intersections and crossings, where braking cars create a smooth surface.
- Spot the hazards. Besides ice, wet fallen leaves can increase the risk of slipping. In spring, winter grit left on road surfaces after snow has melted can cause bicycles to skid.
- Be prepared. Studded tyres improve safety and comfort in winter. Coarsely patterned or deep-grooved tyres are also suitable for winter conditions, but they only provide improved grip on snow.
- Appropriate weather wise clothing improves comfort and safety. Warm shoes, gloves and a helmet hood under your helmet are essential in winter cycling.
In winter, the best storage for bicycles is a dry and cold storeroom. If a bicycle is left in a warm garage in sub-zero weather, it will develop condensation. Condensation in the brake cables can freeze and create a safety risk once back on the road.
Carrying passengers by bicycle
Passengers can be carried only if the cycle has been built or adapted to carry them on a suitable seating. If carrying children in a child seat, check that the seat’s restraining straps are in good condition. The seat should have secure foot straps too.
Make sure the passenger is wearing a suitable cycle helmet.
Passengers can be carried in a trailer too, but take note that towing a trailer will have an effect on the handling of a bicycle especially when turning. When carrying a passenger, the bike must have two separate braking devices.




